I have been using Docker on WSL2 without Docker Desktop for a while now and recently I had to rebuild my Ubuntu distro. I had to go through installing the Docker Engine once again following a series of steps, so thought I would document it so that I can use it again as a reference.
This post is just that and I hope others will find it useful too.
Prerequisites
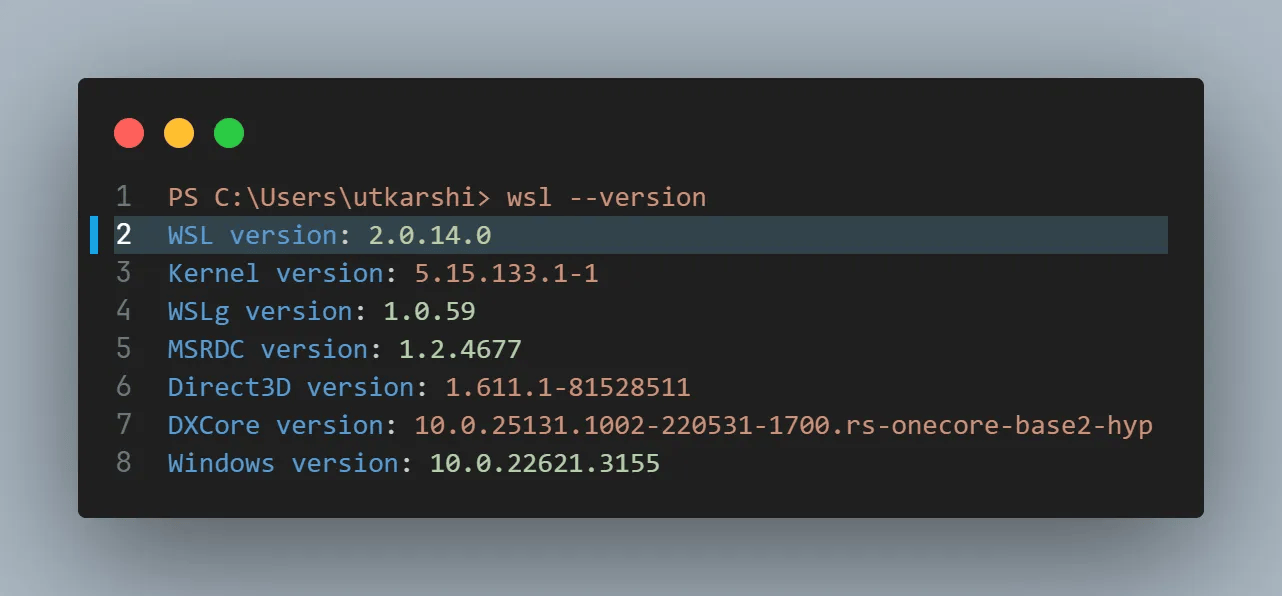
Before installing Docker in WSL2, first make sure you are running WSL2. You can do that using wsl --version in your PowerShell which should output as below.
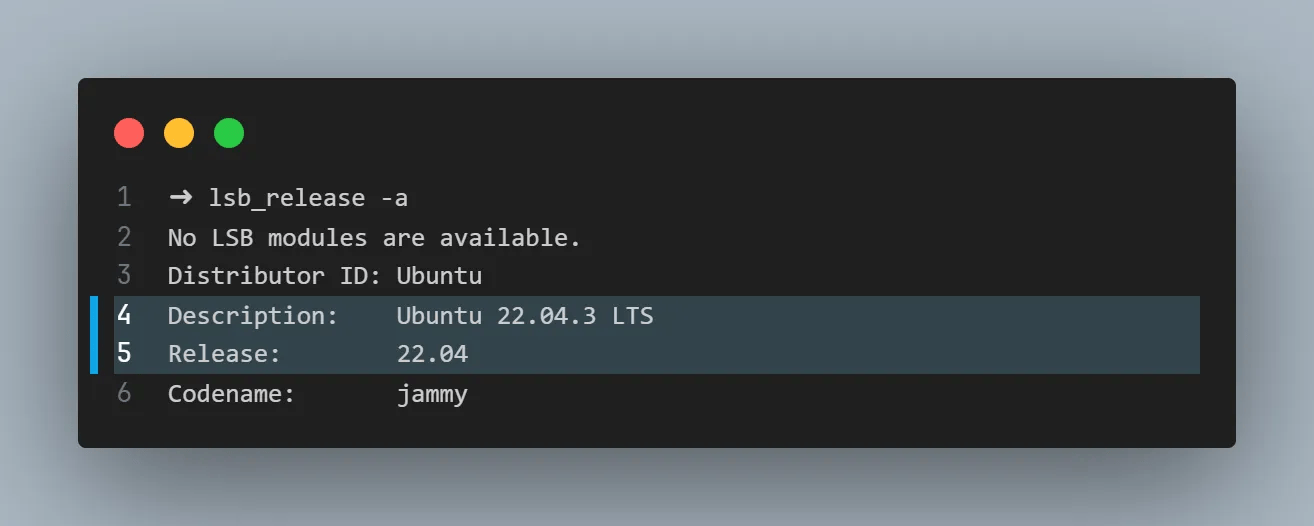
You can also check you are running the Ubuntu version using lsb_release -a command which should output as below
Installing Docker
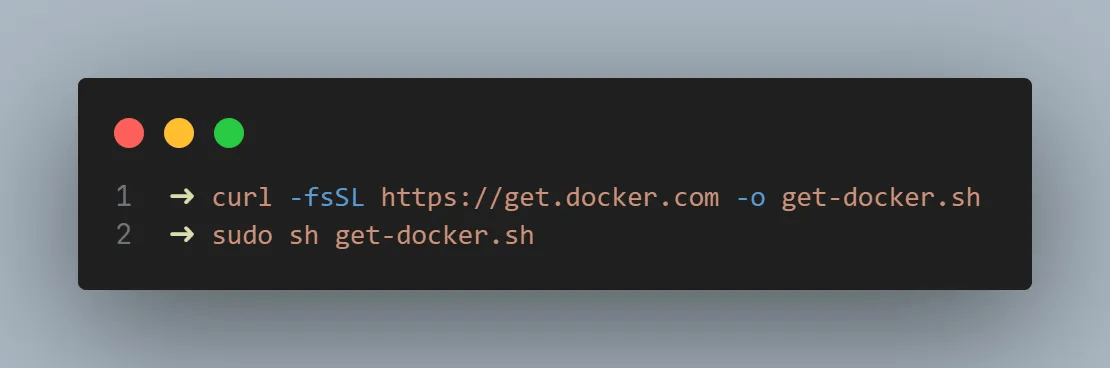
Now that you confirmed you have the prerequisites, let’s start by installing Docker. Docker documentation provides a convenient script for us to run, which just involves running the script below.
However, you might get the error Updates for this repository will not be applied
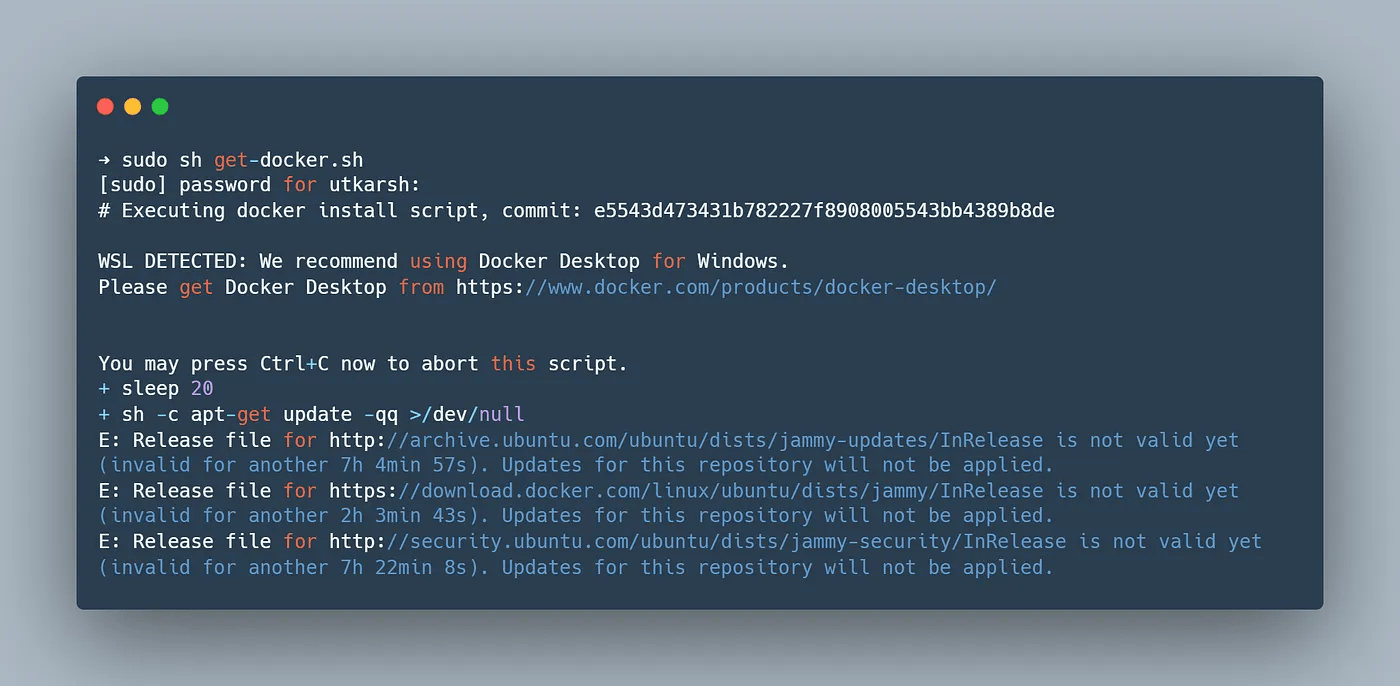
A quick StackOverflow search suggested that this is caused due to the clock being out-of-sync between the Windows machine and the Ubuntu distro running in WSL2. To sync the clock, I had to run sudohwclock --hctosysand restart the WSL usingwsl --shutdown` and start WSL again.
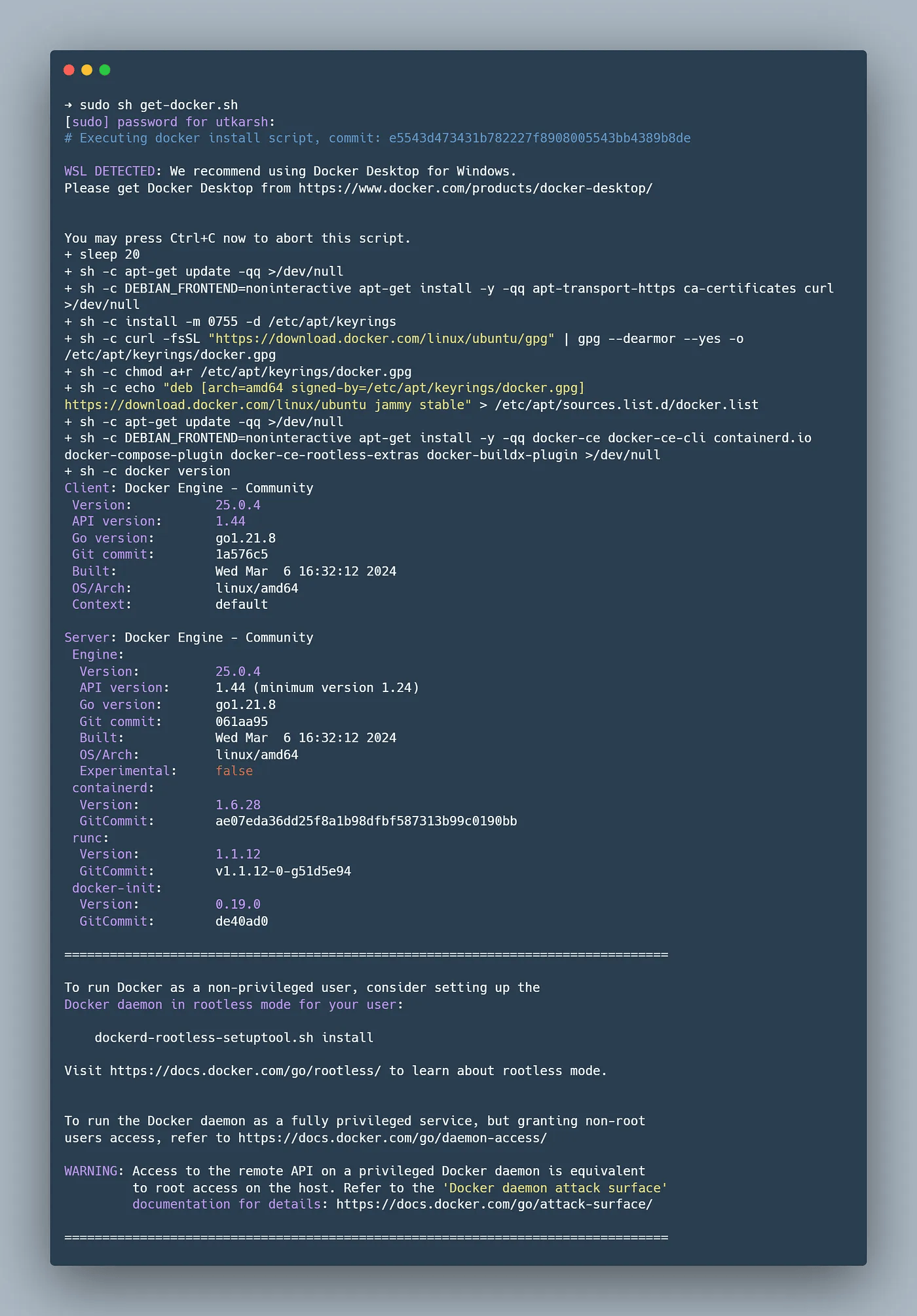
The second attempt to run the command should be successful.
Creating docker group and adding the current user
Due to the way the Unix socket works, we need to preface docker command with sudo. To avoid it, Docker recommends creating a group name docker and adding the current user to it. Docker daemon can then create a Unix socket accessible by members of the docker group.
So, first, create docker group using sudo groupadd docker then add yourself to that group using the command
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
Finally, run newgrp docker to activate the changes to the group.
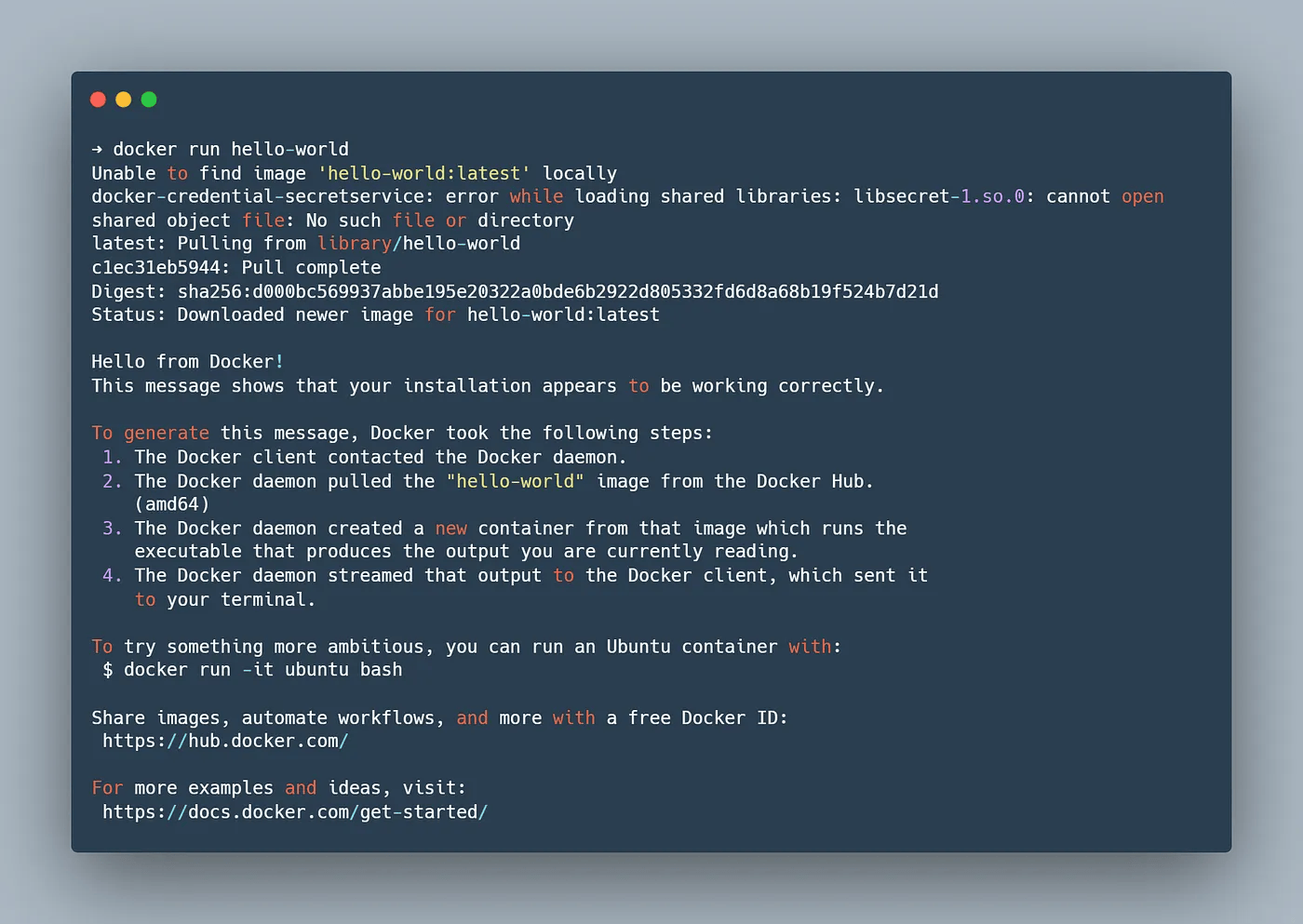
Test running Docker
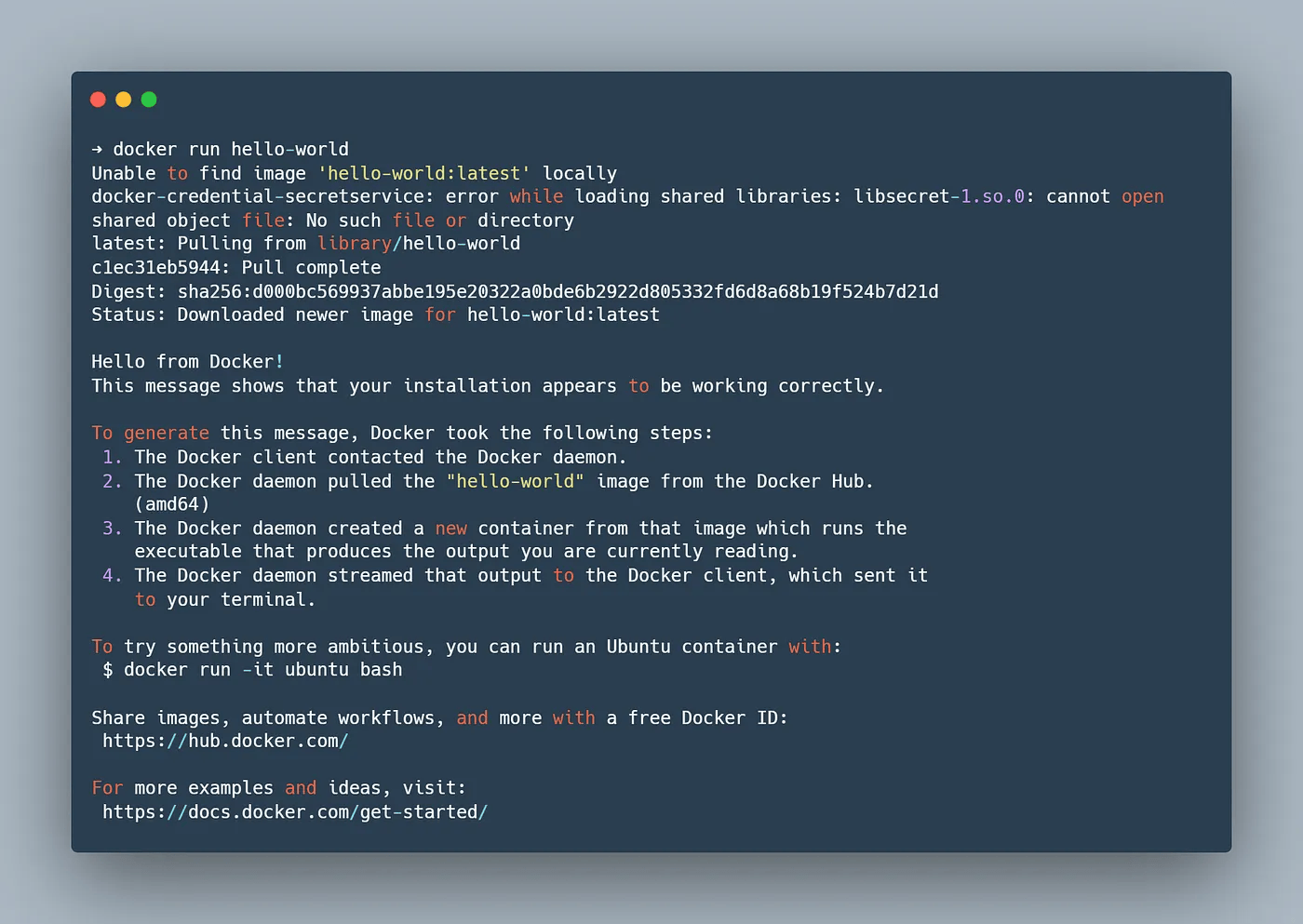
You can now test the docker commands without sudo. Try running docker run hello-world and it should run correctly.
Ensuring Docker daemon starts when you open WSL
Finally, to ensure you have the docker daemon start when you open WSL, you can run the below commands which will start the docker service as soon as you boot.

That is it, you should be able to run all your docker commands without Docker desktop now.